What are the causes of toothache and decay of tooth?
Tooth is the hard, resistant structures occurring on the jaws and in or around the mouth and pharynx areas of vertebrates. Tooth ache or decay may be occur due to high use of sugar content from which our teeth form a layer of caries so let discuss about the dental caries in detail

Dental Caries
Introduction
Dental caries is microbial disease of the calcified tissues of the teeth characterized by demineralization of the inorganic and destruction of the organic substance of the tooth, caused by dental plaque deposits on the tooth surface (plaque is a sticky deposit on teeth in which bacteria proliferate). Frequency and timing of fermentable carbohydrates intake, which will be metabolized by a certain bacteria, such as Streptococcus mutants, bacteria are the culprit of carious tooth, lead to fermentation and therefore produce copious amount of acid and lower the local pH to a level where the minerals of enamel and dentine dissolve. The frequent intake of sweets, dry mouth, and poor oral hygiene may increase the chances for developing new carious lesion. Besides, some risk factors, such as sex, age, dietary habits, socioeconomic, and oral hygiene status, are also associated with increased prevalence and incidence of dental caries in population.
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that 60–90% of children are affected by dental caries. Dental caries affects all age groups, although children are affected to a greater extent than adults.
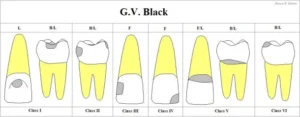
Over 100 years ago, Dr. G.V. Black (1836-1915) developed a system to categorize carious lesions based on the type of tooth affected (anterior or posterior tooth) and the location of the lesion (e.g. lingual, buccal, occlusal, etc.). The six classes of carious lesions according to G.V. Black are as follows:
What symptoms you notice in dental caries person?
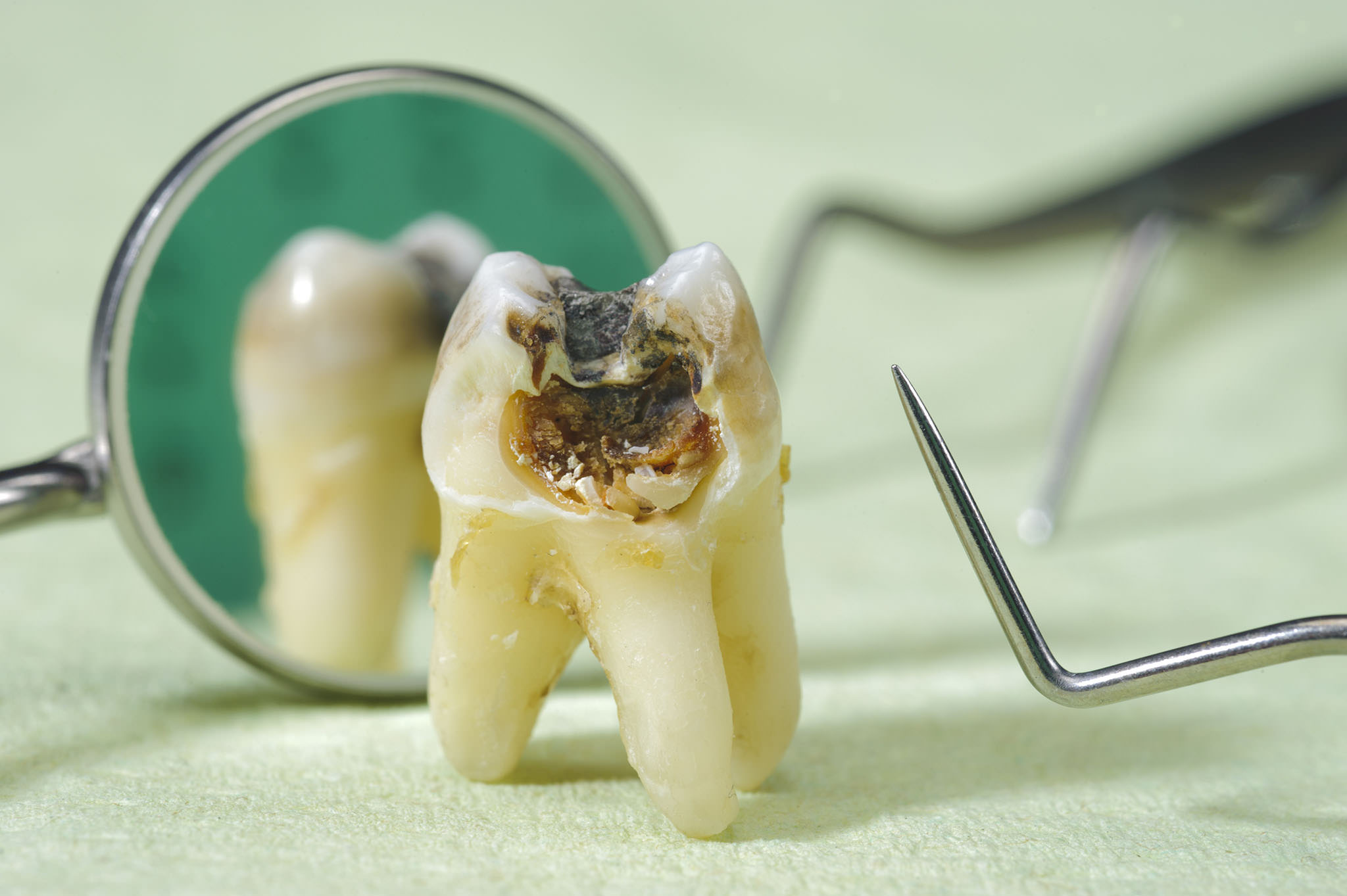
The signs and symptoms of cavities vary, depending on their extent and location. When a cavity is just beginning, you may not have any symptoms at all. As the decay gets larger, it may cause signs and symptoms such as:
- Toothache, spontaneous pain or pain that occurs without any apparent cause.
- Tooth sensitivity
(Mild to sharp pain when eating or drinking something sweet, hot or cold).
- Visible holes or pits in your teeth.
- Brown, black or white staining on any surface of a tooth.
- Pain on chewing.
Early Childhood Caries
Early childhood caries (ECC), also known as “baby bottle caries,” “baby bottle tooth decay” or “bottle rot,” is a pattern of decay found in young children with their deciduous (baby) teeth. This must include the presence of at least one carious lesion on a primary tooth in a child under the age of 6 years. The teeth most likely affected are the maxillary anterior teeth, but all teeth can be affected. The name for this type of caries comes from the fact that the decay usually is a result of allowing children to fall asleep with sweetened liquids in their bottles or feeding children sweetened liquids multiple times during the day.

What are the complications from dental caries?
Dental caries can cause a variety of complications if it’s left untreated. These include:
- Ongoing tooth pain
- A tooth abscess, which can become infected and trigger life-threatening complications, like an infection that enters the bloodstream or sepsis
- The development of pus around the infected tooth
- An increased risk for breaking or chipping a tooth
- Difficulty chewing food
You may cause damage to your tooth that can’t be reversed if you put off seeing a dentist. At this point, the only way to fix the cavity is for your dentist to remove the tooth and replace it with an implant or bridge.
How you can prevent dental caries?
Tooth cavities are a common dental problem, but you can reduce your risk by doing the following:
- Brush your teeth at least twice per day with a fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss at least once daily, as recommended by the American Dental Association.
- Eat fewer sugary and acidic foods, like sweets, candy, juice, soda, and refined carbohydrates.
- Limit snacking between meals.
- Consider getting dental sealants on your teeth.
The following foods can help fight tooth decay:
- Fiber-rich fruits and vegetables
- Calcium-rich foods
- Xylitol sugarless chewing gum
- Unsweetened black or green tea
- Water with fluoride
Regular dental visits and good brushing and flossing habits are your best protection against cavities and tooth decay.
How dental caries diagnosed?
Your dentist can usually detect tooth decay by:
- Asking about tooth pain and sensitivity
- Examining your mouth and teeth
- Probing your teeth with dental instruments to check for soft areas
- Looking at dental X-rays, which can show the extent of cavities and decay
What are treatment options?
Treatment of cavities depends on how severe they are and your particular situation. Treatment options include:
- Fluoride treatment
Daily use of fluoride toothpaste is seen as the main reason for the overall decline of caries worldwide over recent decades. Professional fluoride treatments contain more fluoride than the amount found in tap water, toothpaste and mouth rinses. Fluoride treatments may be liquid, gel, foam or varnish that’s brushed onto your teeth or placed in a small tray that fits over your teeth.
- Fillings
Also called restorations, are the main treatment option when decay has progressed beyond the earliest stage. Fillings are made of various materials, such a composite, amalgam etc.
- Crowns
For extensive decay or weakened teeth, you may need a crown — a custom-fitted covering that replaces your tooth’s entire natural crown. Your dentist drills away all the decayed area and enough of the rest of your tooth to ensure a good fit. Crowns may be made of gold, high strength porcelain, resin, porcelain fused to metal or other materials.
- Root canals
When decay reaches the pulp (inner material of your tooth) , you may need a root canal. This is a treatment to repair and save a badly damaged or infected tooth instead of removing it. The diseased tooth pulp is removed, Medication is sometimes put into the root canal to clear any infection. Then the pulp is replaced with a filling.
- Tooth extraction
Some teeth become so severely decayed that they can’t be restored and must be removed. Having a tooth pulled can leave a gap that allows your other teeth to shift. If possible, consider getting a bridge or a dental implant to replace the missing tooth.

General management for Tooth decay:
Treatment options include: Fluoride treatments. If your cavity just started, a fluoride treatment may help restore your tooth’s enamel and can sometimes reverse a cavity in the very early stages. Professional fluoride treatments contain more fluoride than the amount found in tap water, toothpaste and mouth rinses.

Author


Log in
March 7, 2023I have read your article carefully and I agree with you very much. This has provided a great help for my thesis writing, and I will seriously improve it. However, I don’t know much about a certain place. Can you help me?