What are the causes of abnormal growth of hand and feet?
The abnormal growth of hand and feet is due to the hormonal overproduction. The hormones are chemical that release from glands for the control , growth and development of body. So abnormal secretion of growth hormone( the hormones responsible for growth of body) which is release from pituitary gland that located in our brain cause the your some body parts to grow excessively. In children over secretion of growth hormone cause gigantism (excessive growth and tall body) and in adult cause acromegaly (excessive growth and tall body but with some modifications of body parts).
Gigantism and Acromegaly
Def: Gigantism is a very rare condition that happens when a child has high levels of growth hormone (GH) in their body, which causes them to grow very tall.
Def: Acromegaly that happens when an adult has high level of growth hormone in their body, cause them to grow their hand and feet abnormally.
Reason of abnormal growth:
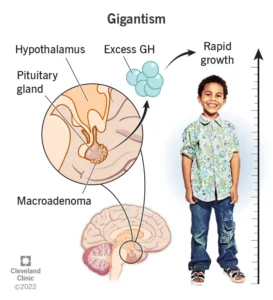
- The pituitary gland normally produces growth hormone, but due to tumor or a cancerous cell or abnormal cell on their pituitary can produce excess growth hormone which results in gigantism if it occurs in childhood but if it occur after maturation than it will cause acromegaly.
- In gigantism, the excessive amount of growth hormone (GH) accelerates the growth of muscle, bones and connective tissue. This leads to an abnormally increased height as well as several soft tissue changes.
What is the difference between gigantism and acromegaly?
- Gigantism and acromegaly are both conditions that result from excess growth hormone (GH). If the growth hormone secretion exceeded in childhood than it is called as gigantism, but if the secretion exceeded in adulthood after maturation than it is called as acromegaly.

What are Signs and symptoms of gigantism:
Excessive amounts of growth hormone (GH) cause the signs and symptoms of gigantism.
- Very prominent forehead and a prominent jaw.
- Gaps between their teeth.
- Thickening of their facial features.
- Large hands and feet with thick fingers and toes.
Other symptoms of gigantism include:
- Enlargement of internal organs, especially your child’s heart.
- Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis).
- Double vision or difficulty with side. (peripheral) vision
- Headache.
- Joint pain .

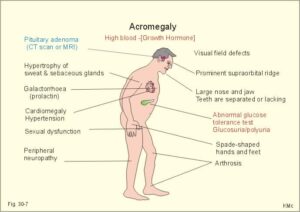
What are the signs and symptoms of acromegaly
The signs and symptoms of acromegaly are
- Enlarged hand and feet.
- Enlarged facial features like tongue, lips and nose.
- Excessive sweating.
- Tiredness and muscle weakness.
- Small outgrowth of skin tissue.
- Pain and limited your mobility .
What is the causes of gigantism and acromegaly:
The most common cause of gigantism and acromegaly are
- Noncancerous) tumor on your child’s pituitary gland that releases excess growth hormone (GH).
- It can also cause when pituitary gland size enlargement .
- Genetic problem like genetic mutation ( abnormal gene) most common gene involved in AIP gene mutation or deletions.
- Acromegaly caused by near by over growth of tissue, suppressing pituitary gland leading to overproduction of hormones and the result is abnormal growth of body.
you may get headaches and vision problems if a tumor pushes against the nearby nerves .
- Acromegaly sometimes runs in families, but most of the time it’s not inherited. Cancer usually spontaneously develop because of a genetic change in a cell of the pituitary gland. This change causes uncontrolled growth of the affected cells, creating the tumor.
Complications of gigantism and acromegaly:
Long-term complications that some people with gigantism might experience due to excessive height and the overall effects of excess growth hormone include:
- Problem in movement or doing work.
- Joint pain.
- Problem in breathing during sleep.
- Enlarged heart (cardiomegaly) and heart valve issues.
- Delayed puberty.
- Irregular menstruation (periods).
- Sleeping problems, such as sleep apnea.
- Muscle weakness.
If your child experiences these symptoms, it’s important to talk to their healthcare provider as soon as possible.
The complications of acromegaly are
- High blood pressure.
- Heart problem most probably enlargement in size.
- Enlargement of thyroid gland.
- Sleep apnea In which difficulty during sleep.
- Vision loss.
- Vertebral column compression.
- High cholesterol.
- Osteoarthritis (joint pain).
- Type 2 diabetes.(high blood sugar level).
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland.
- Precancerous growths on the lining of your colon.
- Inflammation of pancreas.
Risk factors of gigantism:
The risk factor of gigantism are
Genetic disease that affects the skin color (pigmentation) and causes benign tumors of the skin, heart, and endocrine (hormone) system (Carney complex).
Risk factor of acromegaly:
There is no known risk factor for acromegaly other than pituitary tumor.
Tests will be done to diagnose gigantism and acromegaly;
1 Growth hormone and IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1) blood tests.
2 Glucose tolerance test.
3 Sleep study test.
4 MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan or CT (computed tomography) scan .
How is gigantism diagnosed?
Gigantism can be difficult to diagnose due to how rare it is and because growth rates can vary widely from child to child due to genetics and environmental factors.
In general, healthcare providers suspect gigantism when a child’s height is three standard deviations above the normal average height for their sex and age or two standard deviations above the adjusted average based on the height of their biological parents.
If your child’s healthcare provider thinks they may have gigantism, they’ll likely recommend you see an endocrinologist, a healthcare provider who specializes in hormone-related conditions. They’ll make a diagnosis based on your child’s medical and family history, a thorough clinical evaluation and specialized tests such as blood tests and imaging tests.
Gigantism treatment:
The goals of treating gigantism include:
- Safely controlling growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) levels.
- Controlling pituitary tumor growth.
- Reducing the effects of the pituitary tumor on nearby structures, such as brain tissue and the optic nerve.
- Treating or reducing the effects of GH on other body systems.
Surgery for gigantism:
Surgery is the most common treatment option for gigantism. The goal is to remove or reduce the size of the pituitary tumor. Since the pituitary tumors that cause gigantism are often large, children with gigantism may need multiple surgeries to remove the tumor and effectively control GH levels.
Acromegaly treatment:
Acromegaly can be treated by
- Medication
Medicine can suppress the secretion of hormones secretion. Medications may be used as initial treatment if surgery is unavailable or if the person is unable to tolerate surgery.
- Surgery
Microsurgery is done to remove the abnormal growth of pituitary gland due to which over secretion is control.
- Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is done when surgery is not responding well. Radiation decrease the secretion of growth hormone.
Prevention of acromegaly and gigantism:
There is no any prevention for both of the condition treatment can prevent the diseases.
Author


