What are the most common cause of partial blockage of bleeding in urine
If a person feeling obstruction in urination, pain during urination having bleeding in urination and have no control over urination It may be due to any reason like Urinary track infection , kidney problem, ureter problem and prostate gland enlargement.
Prostate enlargement:
It is the one of the most common problem in old age in men. Prostate enlargement means the gland has grown bigger. It is also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia.
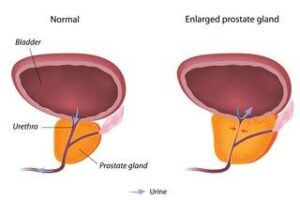
Benign (not that much serious)prostatic hyperplasia (increase in size) (a gland which is only found in male and help in making fluid that have ability to fertilize egg) — is a common condition as men get older. An enlarged prostate gland can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms, such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder (a hollow organ where urine can store). It can also cause bladder problem such as leaking of urine, back flow of the urine and kidney problems.
Before further discussion we should know what is prostate and what are the functions of it.
What is prostate?
The prostate is a gland located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum( part of large intestine). It is about the size of a walnut and surrounds the urethra (the tube that empties urine from the bladder). It produces fluid that makes up a part of semen.
Functions of prostate:
The prostate’s most important function is the production of a fluid that together with sperm, makes up semen. The muscles of the prostate also ensure that the semen is forcefully passed into the urethra ( a thin muscular tube for passage of sperm and urine) and then expelled outwards during ejaculation.
Benign prostate enlargement (BPE) is the medical term to describe an enlarged prostate, a condition that can affect how you pee (urinate).
What is the reason of prostatic enlargement?
The cause of prostate enlargement is unknown, but it’s believed to be linked to hormonal changes as a man gets older. The balance of hormones in your body as you get older get disturbed the gland may get hyperactive and produce too much of hormone or may get any obstructions so the hormone can not release. This may cause your prostate gland to grow.
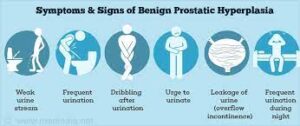
Early signs of prostate disease:
Frequent Urination
Having to urinate again every 2 hours or less
after finishing urinating.
Nocturia
Waking up two or more times at night to urinate.
Incontinence
involuntary loss of urine.
Hesitancy
Difficulty starting or
maintaining a urine
stream.
Urgency
A sudden urge to
urinate that you
can’t control.
Retention
Unable to completely empty the bladder after finishing urinating.

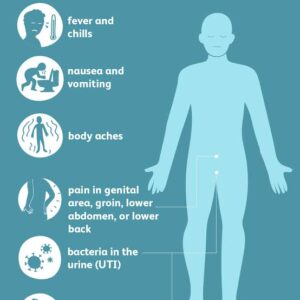
Symptoms of prostate enlargement:
If the prostate becomes enlarged, it can place pressure on the bladder and the urethra,( which is the tube helps the urine to pass through) and the dripping of urine or leakage of urine, have no control over the desire of urine.
This can affect how you pee and may cause:
- Finding it difficult to start peeing
- Straining to pee
- Having a weak flow of urine
- “stop-start” peeing
- Needing to pee urgently and/or frequently
- Urinary tract infection
- Blood in the urine
- Needing to get up frequently in the night to pee
- Accidentally leaking urine (urinary incontinence) Leaking urine can also happen when you do any physical activity. For example, when you cough, sneeze or lift a heavy object. It may cause the leaking of urine. This is called stress incontinence.
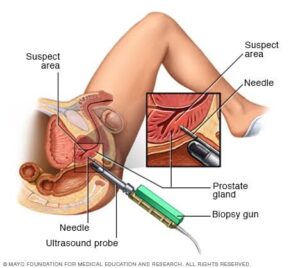
How to Diagnose benign prostatic enlargement:
Your doctor will start by asking detailed questions about your symptoms and doing a physical exam. This initial exam is likely to include:
- Digital rectal exam: The doctor inserts a finger into the rectum to check your prostate for enlargement.
- Urine test: Analyzing a sample of your urine can help rule out an infection or other conditions that can cause similar symptoms.
- Blood test: The results can indicate kidney problems.
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test: PSA is a substance produced in your prostate. PSA levels increase when you have an enlarged prostate. However, elevated PSA levels can also be due to recent procedures, infection, surgery or prostate cancer.
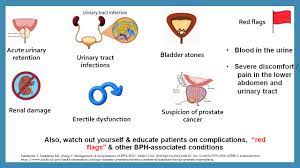
Complications of benign prostate enlargement:
Benign prostate enlargement can sometimes lead to complications, such as:
A urinary tract infection (UTI):
Inability to fully empty the bladder can increase the risk of infection in your urinary tract.
Acute urinary retention:
Acute urinary retention (AUR) is the sudden inability to pass urine and have no control over the urge of urine.
Bladder stones:
These are generally caused by an inability to completely empty the bladder. Bladder stones can cause infection, bladder irritation, blood in the urine and obstruction of urine flow.
Kidney damage:
Pressure in the bladder from urinary retention can directly damage the kidneys or allow bladder infections to reach the kidneys.
When to see a doctor
If you’re having urinary problems, discuss them with your doctor. Even if you don’t find urinary symptoms bothersome, it’s important to identify or rule out any underlying causes. Untreated, urinary problems might lead to obstruction of the urinary tract.
If you’re unable to pass any urine, seek immediate medical attention.
Risk factors :
Risk factors for prostate gland enlargement include:
Age:
Prostate gland enlargement rarely causes signs and symptoms in men younger than age 40. About one-third of men experience moderate to severe symptoms by age 60, and about half do so by age 80.
Family history:
Having a blood relative, such as a father or a brother, with prostate problems means you’re more likely to have problems.
Diabetes and heart disease.
Studies show that diabetes( high blood sugar level), as well as heart disease and use of beta blockers, might increase the risk of BPH.
Lifestyle:
Obesity increases the risk of BPH, while exercise can lower your risk factors.
TREATMENT:
Treatment for an enlarged prostate will depend on how severe your symptoms are.
If you have mild symptoms, you do not usually need immediate treatment. Your doctor will agree with you if and when you need more check-ups.
Life style modifications
You’ll probably be advised to make lifestyle changes, such as:
- Drinking less alcohol, caffeine and fizzy drinks
- Limiting your intake of artificial sweeteners
- Exercising regularly
- Drinking less in the evening
Medicines:
Medicine to reduce the size of the prostate and relax your bladder may be recommended to treat moderate to severe symptoms of an enlarged prostate.
Surgery:
Surgery is usually only recommended for moderate to severe symptoms that have not responded to medicine.
Diet:
Eating more fibre (which is found in fruit, vegetables and wholegrain cereals) can help you avoid constipation, which can put pressure on your bladder and make the symptoms of an enlarged prostate worse.
Bladder training:
Bladder training is an exercise programmed that aims to help you last longer without peeing and hold more pee in your bladder.
Desmopressins Medicine:
Desmopressins medicine slow down urine production so less urine is produced at night.
Prostectomy (surgery to remove prostate gland):
During an open prostatectomy, the prostate gland is removed through a cut in your body. It’s suitable for men who have an enlarged prostate over a certain size.
Author