Why Do People Start Forgetting Things with Age?
Dementia is not specifically a disease but more well describes as a set of symptoms like poor memory, difficulty in learning information, and impaired ability to remember, think and make decisions that interfere with doing everyday activities. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia, and mostly affects adults and older.

Is dementia part of normal aging?
No, many older adults live their entire lives without developing dementia. Normal aging may include weakening muscles and bones, stiffening of arteries and vessels, and some age-related memory changes that may show as:
- Occasionally misplacing car keys.
- Struggling to find a word or things.
- Forgetting the name of any object.
- Forgetting the most recent events.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF DEMENTIA
- Memory loss.
- Difficulty in concentrating.
- Finding it hard to carry out familiar daily tasks.
- Struggling to follow a conversation and start forgetting things in between.
- Being confused.
Mood changes.

Many conditions are progressive, which means that the condition gets worst over time. it starts slowly and gradually but over time it gets worst. In the beginning, a person may show normal symptoms like loss of memory forgetting recent events and names which you should not ignore. take preventive measures and visit the doctor because once the condition gets worst people start forgetting about their home, and their people, and avoid eating, and fecal and urinary incontinence.
Stages of Dementia
Mild Dementia: People forget about small things like names and remain confused.
Moderate Dementia: Memory for the distant past generally seems better, but some details may be forgotten or confused. Be confused regarding time and place. Become lost if away from familiar surroundings. Forget names of family or friends, or confuse one family member with another.
Severe Dementia: Individuals lose the ability to respond to their environment, carry on a conversation, and, eventually, control movement. They may still say words or phrases, but communicating pain becomes difficult.

Causes of Dementia
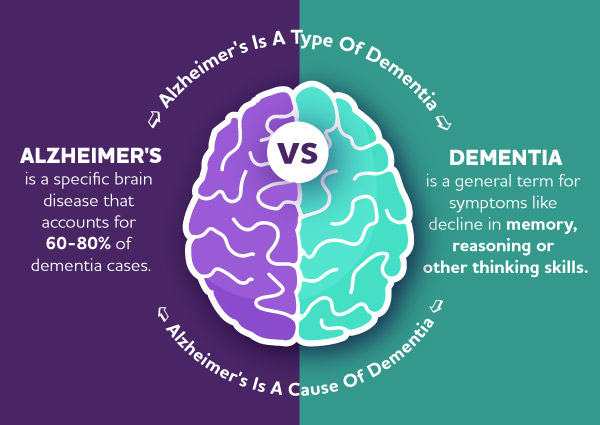
ALZHEIMER DISEASE:

Usually, dementia is caused by some sort of damage to cells in the brain This damage interferes with the ability of brain cells to communicate with each other. When brain cells cannot communicate normally, thinking, behavior, and feelings can be affected.
The brain has many distinct regions, each of which is responsible for different functions (for example, memory, judgment, and movement). When cells in a particular region are damaged, that region cannot carry out its functions normally.
Mostly Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease that cause the generation or loss of neuron in a particular part of the brain.
For example, in Alzheimer’s disease, high levels of certain proteins inside and outside brain cells make it hard for brain cells to stay healthy and communicate with each other. The brain region called the hippocampus is the center of learning and memory in the brain, and the brain cells in this region are often the first to be damaged. That’s why memory loss is often one of the earliest symptoms of Alzheimer’s.
While most changes in the brain that cause dementia are permanent and worsen over time, like thinking and memory problems.
SYMPTOMS:
In the early stages, symptoms might not even be detected but as the disease progress patient have
- Short-term memory loss
- Loss of some motar skills (loss of movement of muscles of the body)
- Language affected face problems to communicate
- Eventually, a patient has long-term memory loss and progressively becomes more disoriented.

What increases the risk for dementia?
Age:
The strongest known risk factor for dementia is increasing age, with most cases affecting those 65 years and older
Genetics:
if any person’s parents or siblings have dementia are more likely to develop dementia themselves.
Race/ethnicity
Older African Americans are more likely to have dementia than whites. Hispanics 1.5 times more likely to have dementia than whites.
Poor heart health
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking increase the risk of dementia if not treated properly.
Traumatic brain injury
Head injuries can increase the risk of dementia, or anything that affect your brain can cause dementia.
DIAGNOSIS:
There is no test to determine if someone is having dementia or not. Doctors diagnose Alzheimer’s and other types of dementia based on a careful medical history, a physical examination, laboratory tests, and the changes in thinking and behavioral changes.
TREATMENT:
Treatment of dementia depends on the underlying cause. Neurodegenerative dementias, like Alzheimer’s disease, have no cure, though there are medications that can help protect the brain or manage symptoms such as anxiety or behavior changes.
Leading a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, healthy eating, and maintaining social contacts, decreases chances of developing diseases and may reduce number of people with dementia.

Author


