HOW CAN YOU GET ASTHMA?
Asthma is a disease of the lung. It is one of the most common long term disease of the children but adults can have asthma too. . It causes your airways to get narrow by producing extra mucus (sticky substance). This makes the breathing difficulty and cause coughing, shortness of breath and produce wheezing sound while breaching.
Asthma can’t be cured, but its symptoms can be controlled. It’s important that you work with your doctor to track your signs and symptoms and take your treatment as needed.

TYPES OF ASTHMA:
There are two types of asthma:
Atopic asthma:
Asthma which is caused by the environmental factors like pollen, dust which trigger the allergens. About 80% of the people who are allergic to asthma have a related condition like hay fever ( it is an allergic reaction to pollen, typically when it comes in contact with your nose mouth eye and throat) eczema (patchy skin with blister cause inching and bleeding) and food allergies.
Non-atopic asthma:
Asthma which is not triggered by any allergens like pollen dust fur. It is less common than atopic asthma. The cause is not well understood and develop later in life, and can be more severe.
What Is an Asthma Attack?
The attack happens in your body’s airways, which are the paths that carry air to your lungs. As the air moves through your lungs, the airways become smaller, like the branches of a tree are smaller than the tree trunk. During an asthma attack, the sides of the airways in your lungs swell and the airways shrink. Less air gets in and out of your lungs, and mucous that your body makes clogs up the airways.

What causes an asthma attack?
We don’t know all the things that can cause asthma, but we do know that genetic, environmental, and occupational factors have been linked to developing asthma.
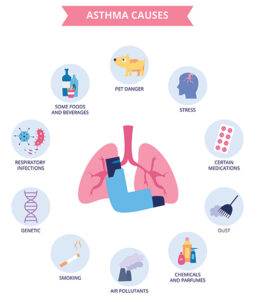
Exposure to various irritants and substances that trigger allergies (allergens) can trigger signs and symptoms of asthma. Asthma triggers are different from person to person and can include:

- Airborne allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, spores, pet dander or particles of cockroach waste. Being exposed to things in the environment, like dampness, some allergens such as dust mites, and second-hand tobacco smoke have been linked to developing asthma.
- Respiratory infections, such as the common cold
- Physical activity
- Cold air
- Air pollutants and irritants, such as smoke
- Certain medications, such as aspirin.
- Strong emotions and stress, some types of foods and beverages, including shrimp, dried fruit, processed potatoes, beer and wine.
Symptoms:
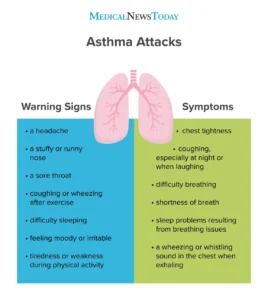
Asthma signs and symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness or pain
- Wheezing sound whlie breathing, which is a common sign of asthma in children
- Trouble in sleeping caused by shortness of breath, coughing or wheezing
- Coughing or wheezing attacks that are worsened by a respiratory virus, such as a cold or the flu.
For some people, asthma signs and symptoms flare up in certain situations:
- Exercise-induced asthma, which may be worse when the air is cold and dry.
- Occupational asthma, triggered by workplace irritants such as chemical fumes, gases or dust
- Allergy-induced asthma, triggered by airborne substances, such as pollen, spores, cockroach waste, or particles of skin and dried saliva shed by pets (pet dander)
When to see a doctor
Severe asthma attacks can be life-threatening. Signs of an asthma emergency include:
- Rapid worsening of shortness of breath or wheezing sound while breathing
- No improvement even after using a quick-relief inhaler
- Shortness of breath when you are doing minimal physical activity contact your doctor.
If you think you have asthma.
If you have frequent coughing or wheezing that lasts more than a few days or any other signs or symptoms of asthma, see your doctor. Treating asthma early may prevent long-term lung damage and help keep the condition from getting worse over time.
Long term asthma:
If you know you have asthma for a long time, work with your doctor to keep it under control and prevent you from life threatening asthma attack.
If your asthma symptoms get worse.
Contact your doctor immediately, if your medication doesn’t provide you relief or use your inhaler immediately. Don’t take any medication without consulting your doctor or without prescription.
Meeting with your doctor:
Meet with your doctor regularly to discuss your symptoms and make any needed treatment adjustments.
How can you develop an asthma:
- Having a family history of asthma like parents, brother and sister.
- Having another allergic condition, such as atopic dermatitis — which causes red, itchy skin — or hay fever — which causes a runny nose, congestion and itchy eyes
- Being overweight
- Being a smoker
- Exposure to second-hand smoke
- Exposure to exhaust fumes or other types of pollution
- Exposure to occupational triggers, such as chemicals used in farming, hairdressing and manufacturing.

How you can prevent asthma:
Take your medicine exactly as your doctor tells you and stay away from things that can trigger an attack to control your asthma. Remember – you can control your asthma. Take your long-term control medicine even when you don’t have symptoms.
If you have asthma, you need to stay away from the things that can trigger asthma. That starts by knowing what causes you to cough, wheeze and grasp for breath. While there’s no cure, there are steps you can take to keep your asthma in control and prevent.
Get vaccinated for influenza and pneumonia. Staying vaccinated can prevent you from flu and pneumonia that trigger asthma.
Identify and avoid asthma triggers. A number of outdoor allergens and irritants such as pollen, cold air and air pollution can trigger asthma attacks. Find out what causes or worsens your asthma, and take steps to avoid them.
Identify and treat asthma early. If you diagnose quickly, you’re less likely to have a severe attack. You also won’t need as much medication to control your symptoms.
Take your medication with your doctor prescriptions. Don’t take medicine without consult from doctor, and even don’t increase or decrease dose without your consult.

Author


