IS THALASSEMIA A SERIOUS DISEASE
Before understanding the word thalassemia you should know about the hemoglobin.
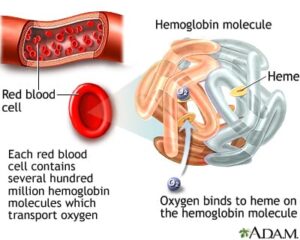
What is hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is red protein that is responsible for transporting oxygen in blood of vertebrates. It is composed of four subunit 2 alpha chains and 2 beta chains that bind with oxygen molecule and transport into the body.
What is thalassemia?
Thalassemia is an inherited (i.e., passed from parents to children through genes) blood disorder caused when the body doesn’t make enough of hemoglobin When there isn’t enough hemoglobin, the body’s red blood cells don’t function properly and they last shorter period of time. Red blood cells carry oxygen to all the cells of the body. Oxygen is a sort of food that cells use to function. When there are not enough healthy red blood cells, there is also not enough oxygen delivered to all the other cells of the body, which may cause a person to feel tired, weak or short of breath. This is a condition called anemia. People with thalassemia may have mild or severe anemia. Severe anemia can damage organs and lead to death.
What are the different types of thalassemia?
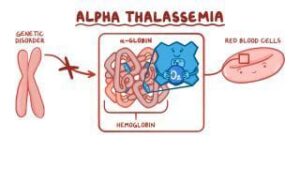
The two types are alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia. The terms alpha thalassemia means hemoglobin have defect or lack alpha subunit and beta thalassemia hemoglobin have defect or lacking in beta subunit.
There are also terms minor and major thalassemia for how severe the thalassemia is, which is noted by words like trait, carrier, intermedia, or major. A person with a trait or minor form may not have symptoms or only mild anemia. Someone with a major form show severe symptoms and may need regular blood transfusions.
Thalassemia is a genetic disease. It pass from parents to offspring in the same way that traits for hair color and body structure are passed down from parents to offspring. The type of thalassemia of a person may depends upon, what type of traits a person received from their parents. For instance, if the mother and father both have thalassemia, person will receive a beta thalassemia trait from his father and another from his mother, he will have beta thalassemia major. You have two genes that are needed to make beta protein. If you have one abnormal copy of the beta gene, you’ll have mild beta thalassemia. If you have two copies, you’ll have more moderate to severe beta thalassemia.
If a mother is only defected with alpha thalassemia and father is normal, person received an alpha thalassemia trait from her mother and the normal alpha parts from her father, she would have alpha thalassemia (also called alpha thalassemia minor). Having a thalassemia trait means that you may not have any symptoms, but you may pass that trait on to your children and increase their risk for having thalassemia. You have four genes responsible for making the alpha protein chain of hemoglobin. You get two from each parent. If you have one abnormal copy of an alpha gene, you won’t have thalassemia but you’ll carry it. If you have two abnormal copies of an alpha gene, you’ll have mild alpha thalassemia. If you have more abnormal copies, you’ll have more serious alpha thalassemia. Babies with four abnormal copies of the alpha gene are often stillborn, or don’t survive long after birth.
Sometimes, thalassemias have other names, like Constant Spring, Cooley’s Anemia, or hemoglobin Bart hydrops fetalis. These names are specific to certain thalassemias – for instance, Cooley’s Anemia is the same thing as beta thalassemia major.
Symptoms of thalassemia:
The signs and symptoms depends upon the type and severity of the condition.
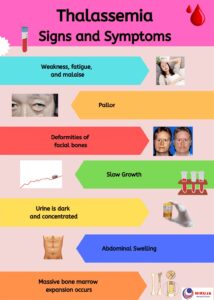
Thalassemia signs and symptoms can include:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Slow growth
- Abdominal swelling
- Dark urine
- Wide and brittle bones
- poor appetite
- spleen enlargement (an organ that filters the blood)
- facial bone deformity
Some people don’t show any symptoms with minor thalassemia and some have even worst condition start appearing even at the time of birth.
How do I know if I have thalassemia?
Some people don’t show the symptoms at all with minor type but some face critical conditions from birth. People with minor condition may only find out with mild anemia feel fatigue hemoglobin level less than normal. People with major type show all the symptoms and may get in blood test that they have thalassemia major and have to get blood transfusion.
Complications of thalassemia:
Iron overload.
People with thalassemia get overloaded with iron because of blood transfusions. Too much iron can result in damage to your heart, liver and other systems.
Infection:
People with thalassemia have an increased risk of infection. Because their spleen get defected which produce Infection fighting cells.
Bone deformities.
Thalassemia can make your bones to widen. This can result in abnormal bone structure, especially in your face and skull and increase the chance of broken bones .
Enlarged spleen:
The spleen produce the infection fighting cells and helps your body to fight with infection. It also cause the destruction of old or damaged blood cells which causes the spleen to enlarge and work harder than normal.
An enlarged spleen can make anemia worse, and it can reduce the lifespan of transfused blood . If your spleen grows too big, your doctor might suggest surgery to remove it.
Slowed growth rates:
Anemia can both slow a child’s growth and delay puberty.
Heart problems:
Congestive heart failure and abnormal heart rhythms can be associated with severe thalassemia.
Can I prevent thalassemia?
Because thalassemia is passed from parents to children, it is very hard to prevent. However, if you or your partner are carrier of thalassemia and want to have child u can talk to the counsellor.
Author


